Blockchain technology will have a profound effect on the market research industry and other businesses around the world. Companies are racing to implement blockchain for the benefits this technology provides. In a recent study by Price Waterhouse, 84% of executives surveyed say they have or are putting a plan to implement blockchain for the future.
But what is blockchain?
Blockchain is a system for storing transaction information in digital blocks. The name comes from the fact that blocks contain three key items – time stamped records of valid transactions, a “hash” or digital fingerprint of the block and a hash of the previous block. In this way any block is linked or chained to the previous block thus forming a “Block-Chain”.
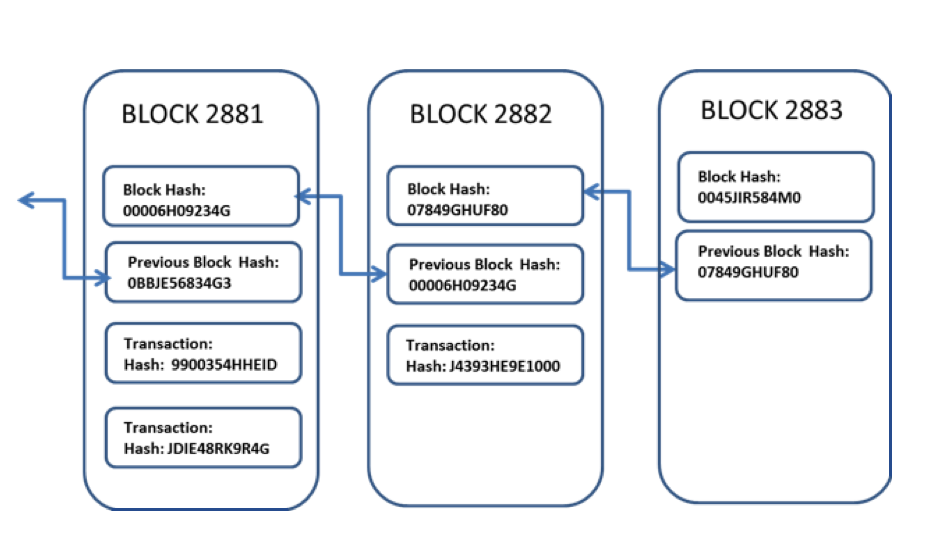
Why the excitement?
Why are Walmart, JP Morgan, IBM, and other companies around the world using blockchain technology?
BECAUSE IT WORKS!
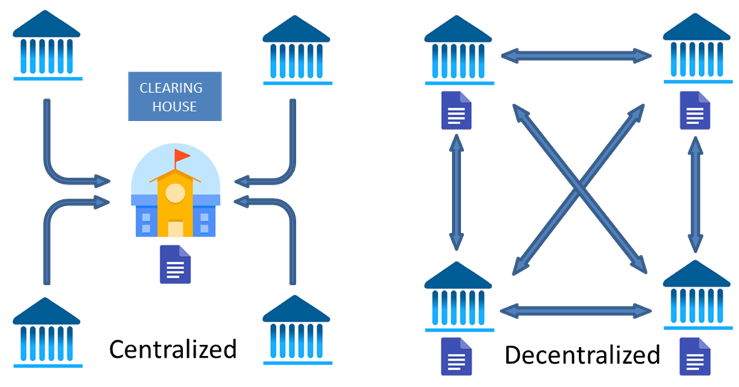
Through blockchain’s decentralised ledger system, individuals and corporations can be confident that financial transactions or information on blockchain are auditable and immutable.
Blockchain’s decentralised ledger system means that all peers or “nodes” of the system possess the same copy of a ledger. These ledgers contain records of the blocks. A majority consensus must be reached before a new transaction is “approved” and recorded in the newest version of the ledger. Fraudulent changes in accounts are nearly impossible without this consensus. Contrast this to the traditional “clearing house” of information where one only has to hack into a single predetermined keeper of the records to steal information.
Companies look for blockchain and decentralised ledgers to provide time savings, cost savings and tighter security:
Time savings: for industries that rely on transaction settlement by a central authority and/or whose transaction times are long because of multi-party interactions, blockchain cuts processing times from days to seconds.
Example 1: Time savings
Walmart is able to track its supply chain to detect bad produce in 2 seconds versus 6 days using blockchain.
Cost savings: companies can realise cost savings from blockchain in several ways:
- The peer to peer self-policing by a permissioned blockchain where only approved members are allowed to share and transact information allows for less oversight.
- Blockchain can reduce layers of intermediaries because participants can exchange items of value directly.
- Duplication of resources to verify transactions is eliminated because all participants already have access to a shared ledger.
Example 2: Cost savings
JP Morgan Chase is implementing an international settlement blockchain with it’s own cryptocurrency to complete crossborder transactions without inefficient intermediaries
Tighter security: members’ only blockchain contains security features to protect against tampering. The blockchain provides for proof that members are who they say they are and that goods or assets traded are verified.
Example 3: Secure and expedited transaction among blockchain members
Cathay Pacific Airlines is using a blockchain decentralized ledger system to expedite redemption of reward points given their numerous vendor partners.
And what does this mean for market research?
Like other industries, the market research industry possesses less than optimal operating processes, data silos, and transactional inefficiencies. These industry issues manifest themselves in what are recognised pain points:
- Poor participation rates
- Poor quality
- Privacy concerns
Blockchain technology is uniquely qualified to address all three of these major pain points. Here is an overview of what emerging companies are doing to shape the market research industry:

Participation rates: Market research technology companies are creating platforms to issue blockchain tokens that represent consumer data as an asset. Instead of consumers providing their data for free, they are compensated with tokens proportionate to the quantity and quality of data they provide. Personal data is now owned by the consumer in the form of tokens and placed in accounts accessible only by the consumers – instead of data aggregators.
The goal of such a platform is to make consumers feel like they gain a greater benefit for providing their insight and personal data and are therefore more likely to participate in market research studies.

Poor quality: Market research technology companies are working on different solutions to poor quality research data. One solution is a better compensation framework combined with a validation process that will approve payment using blockchain smart contracts. Payment is only disbursed when the smart contract detects that all prior agreed upon conditions, such as filling out a survey correctly, are met.
A live pilot run by PREDIQT shows how filters executed through blockchain smart contracts can significantly reduce sample straight-liners and speedsters:
Table 1: Reduction in survey respondent infractions
| Infraction | Survey Question # | Data Set A | Data Set B | % Drop of Infractions |
| Straight-liner cases | Q2 | 20 | 12 | 40% |
| Straight-liner cases | Q3 | 33 | 11 | 67% |
| Straight-liner cases | Q2 & Q3 | 12 | – | 100% |
| Speedster cases (<=3min) | Time Stamp | 14 | 2 | 86% |
| IP Duplicates | IP Address | 20 | – | 100% |
Data Source: PREDIQT and CINT
In this A/B test, the number of infractions (straight-liners, speedsters and repeat survey takers) are tabulated for questions in a control survey – results in data set A. Data set B demonstrates the reduced number of infractions after the blockchain “filters” have been applied to achieve the same sample size.
Another approach being worked on entails KYC or “know your consumer”. Sample buyers want to eliminate duplicate respondents when they purchase from different sources. One technology company is engaging the industry to pilot universal IDs for research participants. Research companies that own a database of consumer information would act as “nodes” of a decentralised ledger system. Universal IDs would be utilised among the “nodes” as a way to share their ledger of consumer data in a matched and coordinated way. These universal IDs would also be tethered to data repositories, providing the industry with more complete demographic and consumer insight into uniquely identifiable respondents.

Privacy: As with other industries, data security has become a priority for the market research industry. News of hacks into databases that contain sensitive personal data is reported on a daily basis. Like a front door with a cheap lock, the centralised data stores of consumer information are inviting to data thieves. Technology companies are looking to use decentralised solutions to break databases into separate pieces and distribute them across an entire network of computers. Such a decentralised database would lack a central control point making it a good deterrent to intrusion. Because blockchain solutions are decentralised, encrypted, and cross-checked by the whole network it would be more difficult to hack. Look for the market research industry to implement decentralised ledger technology to protect its data assets.
The future
In the near term, look for market research technology companies to continue working to fix our industry’s pain points. These solutions will involve some form of issuance of a “token” to provide liquidity to personal data as an asset, the empowering of consumers to own their data, and the injection of efficient processes for transactions and verification. Look also for solutions that involve the creation of KYC (know your consumer) platforms and solutions using decentralized ledger systems to improve data security.



1 comment
great and simple